Blue Hydrogen
10/01/2025
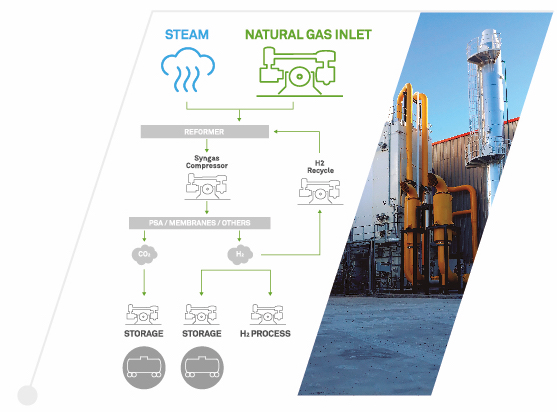
Blue hydrogen is a hydrogen type obtained from natural gas as a raw material, with the goal of minimizing carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions generated during its production. This process is done by the capture and storage of CO₂ (CCS technology, Carbon Capture and Storage), preventing its release into the atmosphere.
1. Steam Methane Reforming (SMR)
Steam methane reforming is a widely used technology for producing hydrogen from natural gas (methane). This process operates under high-temperature (700–1,000 °C) and high-pressure conditions, where methane reacts with steam in the presence of a catalyst, generating synthesis gas (syngas). This gas mainly consists of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
The syngas produced in the reformer is compressed using a syngas compressor. This increases its pressure so it can be processed in separation systems such as PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption), membranes, or other technologies.
2. Component Separation: Hydrogen Purification
In the separation stage, the compressed gas enters a PSA system or an alternative such as membranes.
In PSA, adsorbent materials retain unwanted gases, such as CO₂, while allowing hydrogen to pass through the system as pure gas.
The purified hydrogen is directed for its final use, while the separated CO₂ is channeled for capture and storage.
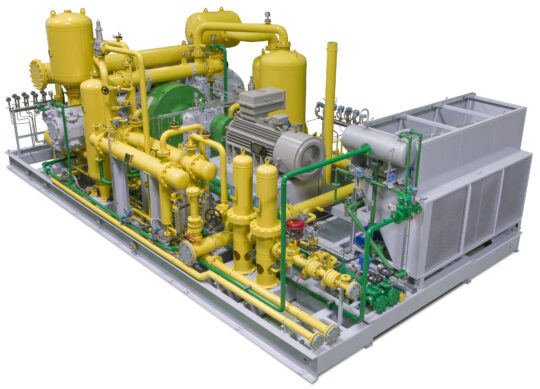 Synthesis gas compresor
Synthesis gas compresor
3. CO₂ Capture and Compression
The recovered carbon dioxide is compressed using a CO₂ compressor, enabling:
-Its storage or capture.
-Its use in industrial applications, such as carbonate production or chemical processes.
This step ensures that the process meets the requirements to be classified as blue hydrogen by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
 CO₂ Compressor
CO₂ Compressor
4. Hydrogen Recirculation
A portion of the purified hydrogen is recirculated to the reformer via a hydrogen compressor. This recirculation improves the overall efficiency of the reformer, as hydrogen acts as a reducing gas that optimizes internal chemical reactions.
5. Hydrogen Storage and Transport
The remaining purified hydrogen is compressed using a hydrogen compressor for:
-Storage in pressurized tanks.
-Transport to industrial or energy applications, such as fuel cells, heat generation, or ammonia production.
Each of these stages is interconnected and optimized through the use of specific compressors, which ensure the appropriate pressure and system efficiency at each point in the process.
Compressors Used in the Blue Hydrogen Production Process:
1. Natural Gas Compressor: Used to compress and inject natural gas into the steam methane reformer (SMR).
2. Syngas Compressor: Once the syngas is obtained in the reformer, a syngas compressor is required for injection into a PSA system or other separation and purification technologies.
3. CO₂ Compressor: Facilitates the capture and compression of carbon dioxide generated during the purification process in the PSA.
4. H₂ Compressor for Recirculation: Used to recirculate hydrogen back into the reformer, improving its efficiency.
5. H₂ Compressor for Storage or Processing: Allows the compression of the obtained hydrogen for subsequent storage or treatment according to process requirements.
 Hydrogen compressor
Hydrogen compressor
At ABC Compressors, we are experts in gas compression solutions with proven experience across all the compressor types mentioned. If you’re ready to take the next step into the Blue Hydrogen industry, don’t hesitate to contact us.
Noticias
relacionadas
Apr
Proyecto Atmosphere
Nov
New app from Coca Cola Austria rewards consumers for recycling PET bottles
From next year, if Coca-Cola customers in Austria check-in at a collection container, scan a code …
Mar
Proyecto ZL-2023/00244 – RECCOM
-
CERTIFICACIONES
-

-

